Alignment in Anchor Positioning using position-area
The position-area property allows you to control the placement of an absolutely positioned element relative to its anchor box. It considers a 3x3 grid defined by the containing block of the absolutely positioned element and the edges of the anchor box.
.anchor {
anchor-name: --a;
}
.element {
position: absolute;
position-anchor: --a;
}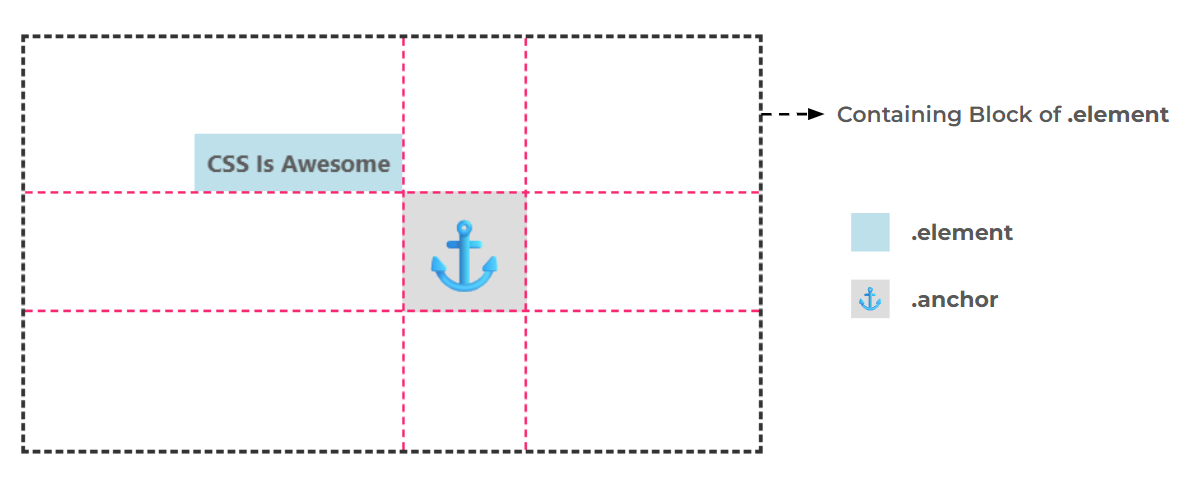
You can select an area that consists of one or more adjacent cells of the grid. That area becomes the new containing block of the absolutely positioned element where it's aligned.
Here is an interactive demo where you can select an area from among all 36 possibilities and get its code. You can also drag the anchor element and see how the grid behaves.
.element {
position-area: top left;
justify-self: ;
align-self: ;
}I am using a stretch alignment to illustrate the different areas, but you can change it to place the element wherever you want within the selected area.
The normal value is the default value and has an interesting behavior. It places the element as close as possible to the anchor, which is what you will want in 90% of cases, so you will rarely need to update the alignment.
The anchor-center is a special value different from center. center considers the center of the selected area, while anchor-center considers the center of the anchor in the relevant axis.
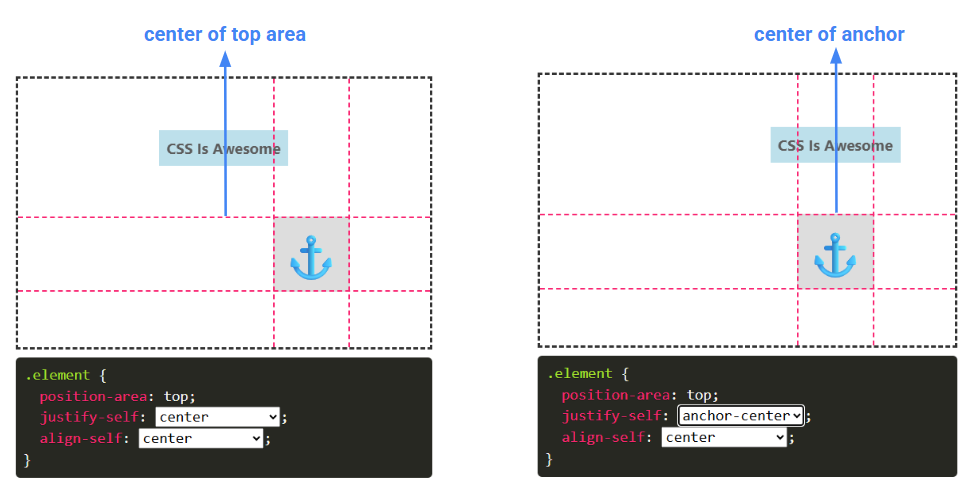
anchor-center is a safe alignment value. If centering is not possible, the element will shift to remain within the selected area.
More details about alignment: The Fundamentals of CSS Alignment
More CSS Tips
- Responsive List of Stacked/Overlapping Images A few lines of modern CSS to create a horizontal list of responsive stacked images.
- The Universal Focus Ring Using anchor positioning to create a fancy focus ring that travels the whole page.
- Conditional Border Radius with Modern CSS A simple trick to control the border-radius based on the screen/container size.
- Dynamic Tooltip Position with Anchor Positioning A tootlip that follows its anchor while adjusting the position of its tail.